How the Mid-Market Rate Impacts Cross-Border Transactions: A Guide for Global Businesses

Introduction
In today’s global economy, cross-border transactions are a routine part of doing business. From international vendor payments to remote employee salaries and global subscription billing, businesses are moving money across currencies more than ever before.
But there’s a hidden detail in these money transfers that can make a big difference: the exchange rate, which is how much one currency is worth when converted into another. Not all exchange rates are the same. Some providers may not give you a good deal—they might charge you more than the fair rate, which is called the “Mid-Market Rate".
In this article, we’ll explain what the mid-market rate really means, how extra charges added by currency exchange services (called FX markups) can eat into your profits, and why knowing about this can help companies make smarter financial decisions when dealing with international payments.
What Is the Mid-Market Rate?
The mid-market rate also known as the real exchange rate or interbank rate is the midpoint between the buy and sell prices of a currency pair in the global foreign exchange (FX) market.
Imagine a bank:
Buys 1 USD for ₹83.40
Sells 1 USD for ₹83.60
The mid-market rate = ₹83.50
The mid-market rate is simply the middle point between the buy and sell rates.
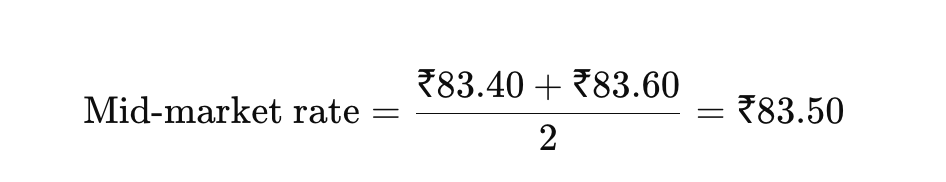
This is the most neutral, transparent rate available the one you’ll typically find on Google, Bloomberg, or XE. It reflects the true value of one currency against another, free of any fees, markups, or institutional profit margins.
Why it matters?
It’s the rate used when banks trade amongst themselves. If you can get close to this rate in your international transactions, you’re getting a better deal and keeping more of your money.
The FX Markup: A Hidden Cost for Global Businesses
While the mid-market rate offers a transparent benchmark, most banks and payment providers do not offer it to their customers. Instead, they add a markup or spread often without clearly disclosing it.
For example:
- Mid-market rate: $1 = ₹83.50
- Bank-offered rate: $1 = ₹82.80
- Hidden FX cost: ₹0.70 per USD
A ₹0.70 difference on a $100,000 international transfer results in a ₹70,000 loss, without any line item in your invoice to explain it.
Why This Matters for International Businesses
For any business involved in cross-border trade or operations, FX costs are not a minor issue — they affect profitability, forecasting, and competitiveness.
1. Hidden Margin Losses: Even a 0.5–1% FX markup can lead to tens of thousands of dollars in annual losses, particularly for companies processing large vendor payments or global payroll.
2. Unclear Financial Reporting: Without transparency in rates, it becomes harder to reconcile actual transaction costs, complicating accounting, tax filing, and audit readiness.
3. Pricing Inconsistencies: If your business accepts payments in foreign currencies or bills customers abroad, poor FX rates may affect how your pricing aligns across markets.
4. Cash Flow Uncertainty: Inconsistent rates can disrupt cash flow projections, especially in volatile currency environments or during high-frequency transfers.
The Mid-Market Rate in International Transactions
While not always accessible directly, the mid-market rate acts as a baseline for evaluating the fairness of any FX offer. Companies that benchmark providers against this rate are able to:
- Improve cost visibility
- Negotiate better terms
- Select more transparent platforms
- Time their conversions more strategically
Advantages of using or referencing the mid-market rate:
- Lower overall transfer costs
- Greater transparency in FX pricing
- Improved financial planning and predictability
- Fairer pricing for customers and partners across borders
- Higher profit retention, especially for exporters and SaaS businesses
Strategies for Leveraging the Mid-Market Rate
Businesses that align themselves more closely with the mid-market rate can unlock both financial and operational advantages.
1. Use Providers That Offer Mid-Market or Transparent Rates
Select platforms that offer either the mid-market rate or minimal spreads with fully disclosed pricing.
2. Leverage Multi-Currency Accounts
Hold and manage balances in multiple currencies to reduce the need for immediate conversion. This enables smarter timing and cost optimization.
3. Automate FX Rate Monitoring
Use automated alerts or APIs to track real-time exchange rates and lock in favorable conversion windows.
4. Hedge Predictable Cash Flows
If your business pays or receives predictable sums monthly in foreign currencies, consider using forward contracts or hedging tools to lock in mid-market–adjacent rates.
5. Audit Your FX Spend
Include exchange rate markups as part of your financial analysis. A few basis points in spread could translate into major budget impacts over time.
Final Thoughts
The mid-market rate is more than a benchmark — it is a lens through which businesses can assess the true cost of international payments.
By referencing or accessing rates close to the mid-market, companies gain:
- Cost control
- Operational transparency
- Greater confidence in global expansion
In a world where every basis point matters, especially for high-volume or recurring transactions, choosing partners and systems that align with the mid-market rate isn’t just financially smart it’s strategically essential.
